Imagine the miraculous journey of a humble bee, from its humble beginnings as a pupa to its vital role as a pollinator. In this captivating article, we will explore the fascinating transformation that takes place within the bee’s cocoon, uncovering the secrets of its metamorphosis into a fully-fledged adult bee. Journey alongside these industrious creatures as they undergo a remarkable process of growth, development, and emergence, ultimately taking flight to play a crucial role in our ecosystems. Prepare to be amazed as we witness the captivating birth of an adult bee!
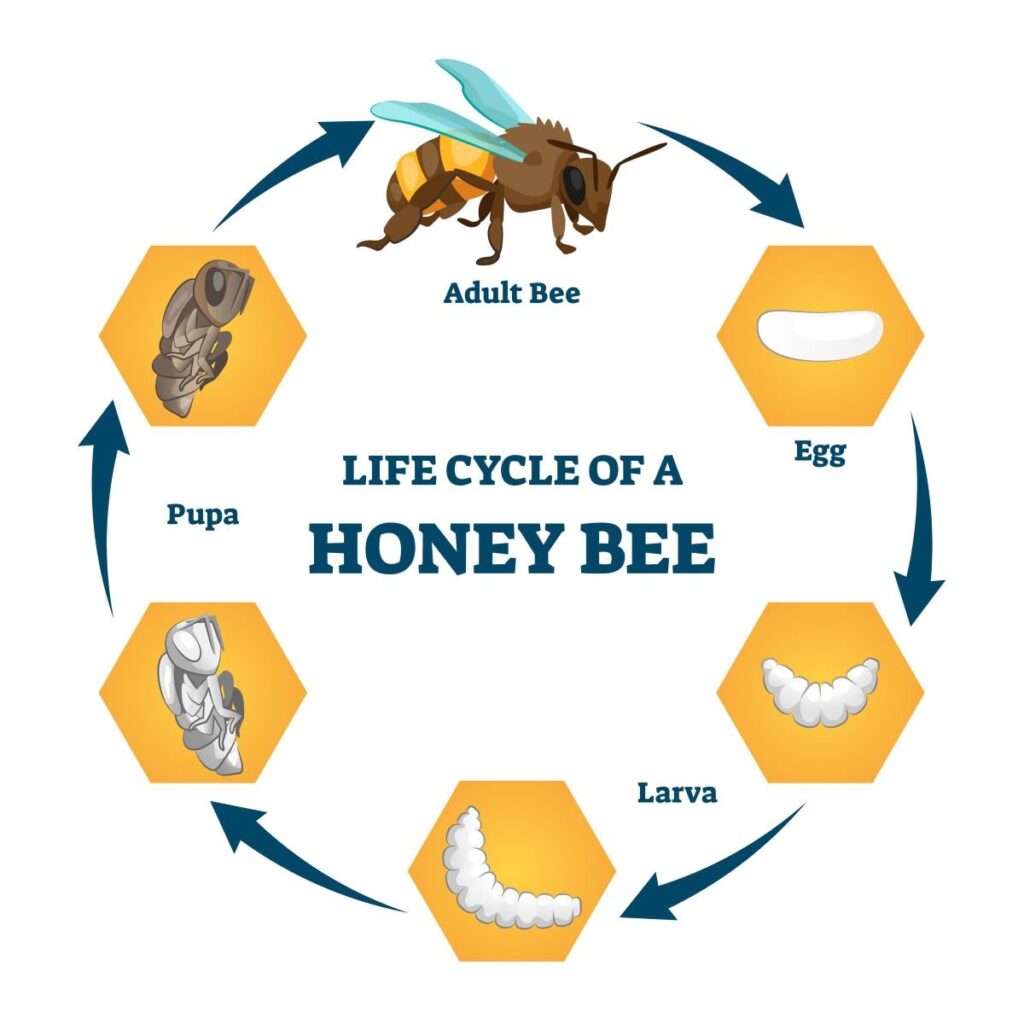
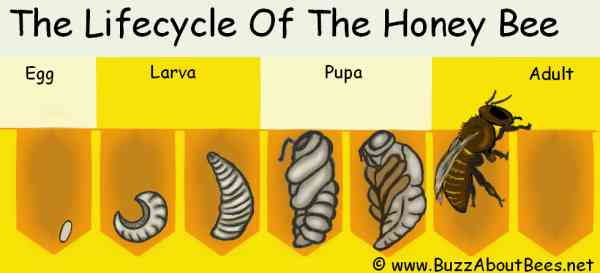
The Life Cycle of a Bee
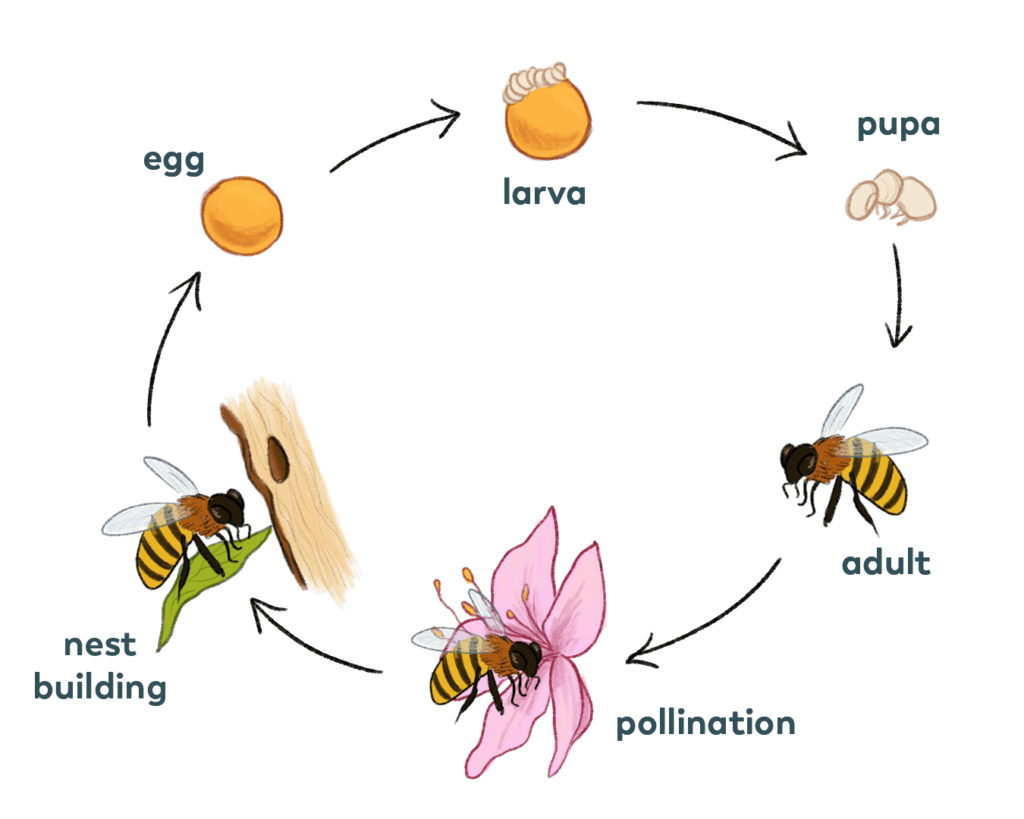
Everyone knows that bees play a vital role in our ecosystem, but have you ever wondered about their life cycle? From the moment an egg is laid to the time an adult bee emerges, these incredible creatures go through several stages of development. Let’s take a closer look at the life cycle of a bee and explore the fascinating journey they embark upon.
Egg Stage
The first stage in the life cycle of a bee begins with the egg stage. This is when the queen bee lays her eggs in honeycomb cells. Each egg is tiny, milky white, and shaped like a grain of rice. The queen carefully chooses the cells where she will lay her eggs, ensuring that they have enough food resources for the growing larvae.
Egg Laying
During the egg-laying process, the queen bee can lay up to 2,000 eggs in a single day. She uses her stinger to deposit each egg at the bottom of a cell. The queen’s ability to lay eggs is truly remarkable and essential for the survival of the bee colony.
Incubation Period
Once the eggs are laid, they enter the incubation period. During this time, the eggs are kept warm and protected by the worker bees. The heat generated by the buzzing wings of the workers helps maintain the optimal temperature for the eggs to develop. The length of the incubation period varies depending on the type of bee, but it typically lasts for a few days.
Larva Stage
After the eggs have hatched, the next stage of the bee’s life cycle begins – the larva stage. During this phase, the bee larvae grow rapidly and undergo significant changes in their appearance and behavior.
Growth and Feeding
As the larvae grow, they consume large amounts of food. The worker bees diligently feed the larvae a mixture of pollen and nectar known as “bee bread.” This nutrient-rich diet is crucial for the larvae’s development and provides them with the energy they need to grow.
Molting
As the larvae continue to feed, their exoskeleton becomes too tight, and they must shed it through a process called molting. Once they have shed their old skin, the larvae continue to eat and grow until they reach their full size.
Pupa Stage
the pupa stage is a transformative period in the life cycle of a bee. During this time, the larvae undergo a remarkable metamorphosis, preparing to emerge as fully formed adult bees.
Prepupa Stage
Before entering the pupa stage, the larvae go through a short prepupa stage. During this phase, the larvae rest in their cells while their bodies prepare for the upcoming metamorphosis. They undergo internal changes as their tissues reorganize, and their bodies begin to take on the shape of an adult bee.
Pupation
Once the prepupa stage is complete, the larvae enter the pupation phase. This is when they undergo the most dramatic changes in their body structure. Inside the cell, the larvae spin a cocoon around themselves using silk threads they produce. This silk cocoon protects them during the transformation process.
Prepupa Stage
During the prepupa stage, the larvae prepare themselves for the final stages of metamorphosis. They develop fully formed wings, legs, and other adult structures. This stage is critical for the successful emergence of an adult bee.
Pupation
As the larvae complete their preparation for metamorphosis, they enter the pupation phase. This is when the transformation from pupa to adult bee truly begins.
Transformation Begins
Inside the cocoon, the larvae’s tissues break down and reorganize, forming adult structures. This process involves the development of wings, legs, eyes, and other specialized body parts. Slowly but surely, the pupa undergoes a complete metamorphosis, transforming into a fully formed adult bee.
Formation of Adult Structures
During pupation, the bee’s body undergoes significant changes. The soft, pale body of the pupa gradually darkens as the external structures of the adult bee develop. Wings become fully formed, and the hairs on the body begin to appear.
Adult Stage
Finally, after weeks of development, the adult bee emerges from its cocoon, ready to take on its role in the colony. This stage marks the culmination of the bee’s life cycle and the beginning of its adult life.
Emergence from Pupa
As the fully formed adult bee emerges from its cocoon, it carefully chews through the silk threads to free itself. Once free, the bee takes some time to rest and allow its wings to unfold and harden. This process is crucial for the bee to be able to fly and navigate its environment successfully.
Maturation
After emerging from the pupa, the adult bee continues to mature over the next few days. During this time, it becomes accustomed to its new body and its role within the colony. The bee’s exoskeleton hardens, and its coloration becomes more vibrant.
First Flight
Once the adult bee has matured sufficiently, it takes its first flight outside the hive. This flight serves several purposes, including orientation and familiarizing itself with the surrounding environment. The bee will also begin its vital tasks of foraging for food and contributing to the reproduction of the colony.
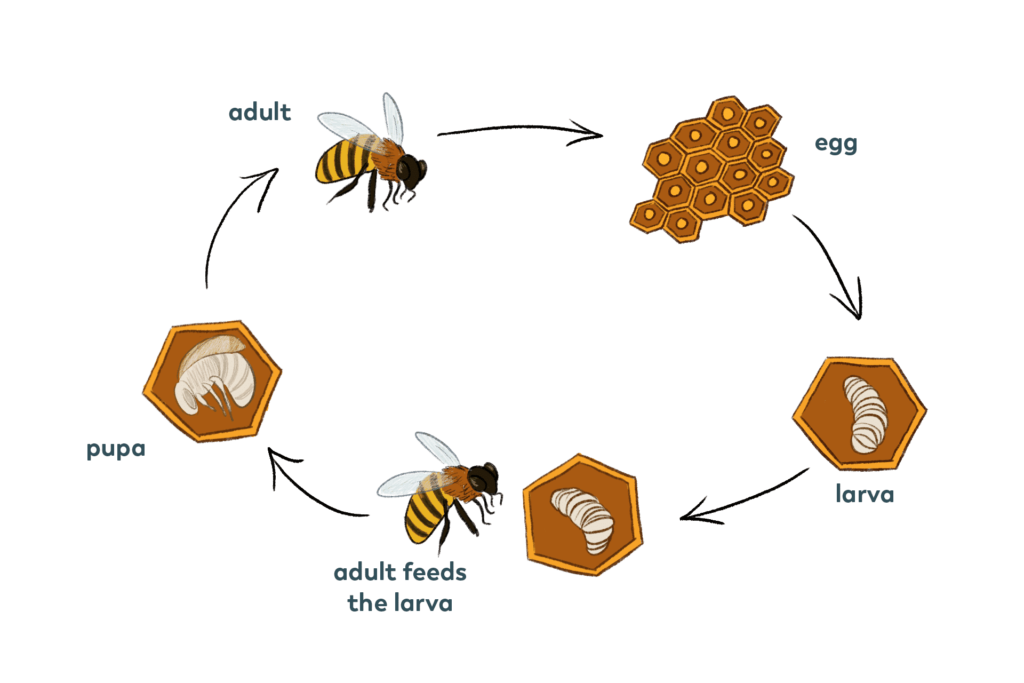
Role of the Adult Bee
Now that the bee has entered the adult stage, it takes on essential roles within the colony.
Foraging for Food
Adult bees play a crucial role in collecting food and resources for the colony. They venture out into the surrounding areas, seeking nectar and pollen from flowers to bring back to the hive. As they visit flowers, they inadvertently transfer pollen, allowing for plant reproduction through the process of pollination.
Reproduction
The queen bee is responsible for laying eggs and ensuring the survival of the colony. However, the drones, male bees, also play a role in reproduction. Their sole purpose is to mate with the queen bee and contribute to the genetic diversity of the colony.
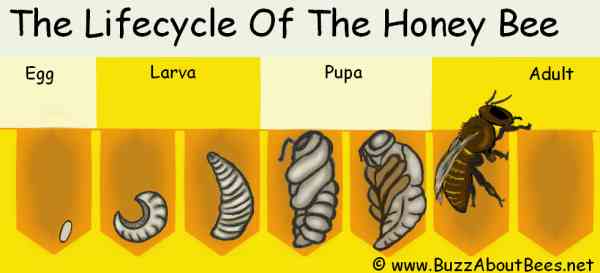
Importance of Bees as Pollinators
Bees are not only fascinating creatures, but they also have a significant impact on the ecosystem and human society as a whole. Let’s explore the importance of bees as pollinators.
Plant Reproduction
Pollination is a crucial process for plant reproduction. Bees, while foraging for nectar, inadvertently pick up pollen on their bodies and transfer it from flower to flower as they move about. This transfer of pollen allows plants to produce fruits, seeds, and other essential reproductive structures.
Ecological Impact
Bees play a vital role in maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance. By pollinating a wide variety of plants, they contribute to the survival of numerous plant species. This, in turn, supports other wildlife that depends on these plants for food and shelter.
Economic Impact
Beyond their ecological importance, bees also have a significant economic impact. They contribute to agricultural productivity by pollinating crops, such as fruits, nuts, and vegetables. The value of bee pollination to global crop production is estimated to be in the billions of dollars annually.
Factors Affecting Bee Populations
Despite their importance, bee populations around the world face numerous threats. Let’s explore some of the factors affecting bee populations.
Loss of Habitat
One of the most significant challenges bees face is the loss of habitat. As urbanization and human activities continue to encroach upon natural landscapes, bees lose access to their native habitats. Destruction of bee-friendly environments, such as forests and meadows, limits their food sources and nesting sites, leading to population declines.
Pesticide Use
The widespread use of pesticides in agriculture poses a significant risk to bee populations. Many pesticides, including insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides, can be toxic to bees and other pollinators. Exposure to these chemicals can weaken bees, impair their reproduction, and even cause death.
Climate Change
Climate change is another factor threatening bee populations. Rising temperatures, changing weather patterns, and extreme weather events can disrupt the delicate balance that bees rely on for their survival. Shifts in flowering times and disruptions in the availability of nectar and pollen can negatively impact bee nutrition and reproduction.
In conclusion, the life cycle of a bee is a remarkable journey that involves several stages of development. From the humble egg to the fully formed adult, bees undergo incredible transformations that are essential for their survival. As pollinators, bees play a crucial role in plant reproduction, ecological balance, and even our own food production. However, they face numerous challenges due to habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change. It is our responsibility to protect and preserve these incredible creatures and ensure their continued existence for the benefit of our planet and ourselves.