
In the fascinating world of bees, there is a group of individuals that often goes unnoticed, yet plays a crucial role in the reproductive success of these remarkable insects. Enter the drones – the unsung heroes of bee reproduction. These male bees may not be as well-known as their female counterparts, but their existence is essential for the survival of the entire colony. In this article, we will explore the fascinating life of drones, their unique characteristics, and the vital role they play in ensuring the continuation of bee populations. Get ready to discover the untold story of these incredible creatures!
Why are Drones Important in Bee Reproduction?
Introduction to drones
Drones are male bees whose primary role is to mate with the queen bee, thus playing a crucial role in the reproductive cycle of honey bees. Although often overlooked, drones are the unsung heroes of bee reproduction. They possess unique characteristics and behaviors that contribute significantly to the genetic diversity and long-term health of the colony. Understanding the importance of drones and their role in bee reproduction is key to appreciating the intricate workings of the honey bee society.
The role of drones in bee reproduction
Drones play an essential role in the mating process of honey bees. Their main function is to fertilize the queen bee, ensuring the continuation of the colony. Without drones, the reproductive cycle of honey bees would come to a halt. The genetic diversity provided by drone mating improves colony resilience, disease resistance, and overall colony health. Therefore, drones are vital for maintaining the balance and survival of honey bee populations.
The mating process of honey bees
The mating process of honey bees is a fascinating and carefully orchestrated phenomenon. It begins with the queen bee leaving the hive in search of a Drone Congregation Area (DCA), where drones from other hives gather. Once the queen reaches the DCA, she releases pheromones to attract and entice the drones. This process ensures that mating occurs between genetically diverse individuals, increasing the chances of a healthy and thriving colony.
The significance of genetic diversity in bee colonies
Genetic diversity in bee colonies is crucial for their long-term survival. It results in increased resistance to diseases and parasitic infestations, as well as improved adaptation to changing environmental conditions. Drones contribute to genetic diversity by carrying genes from different colonies and mating with queen bees from other hives. This genetic exchange ensures a wide range of traits and characteristics, enhancing the overall fitness of the bee population.
Characteristics of Drone Bees
Physical differences between drone bees and worker bees
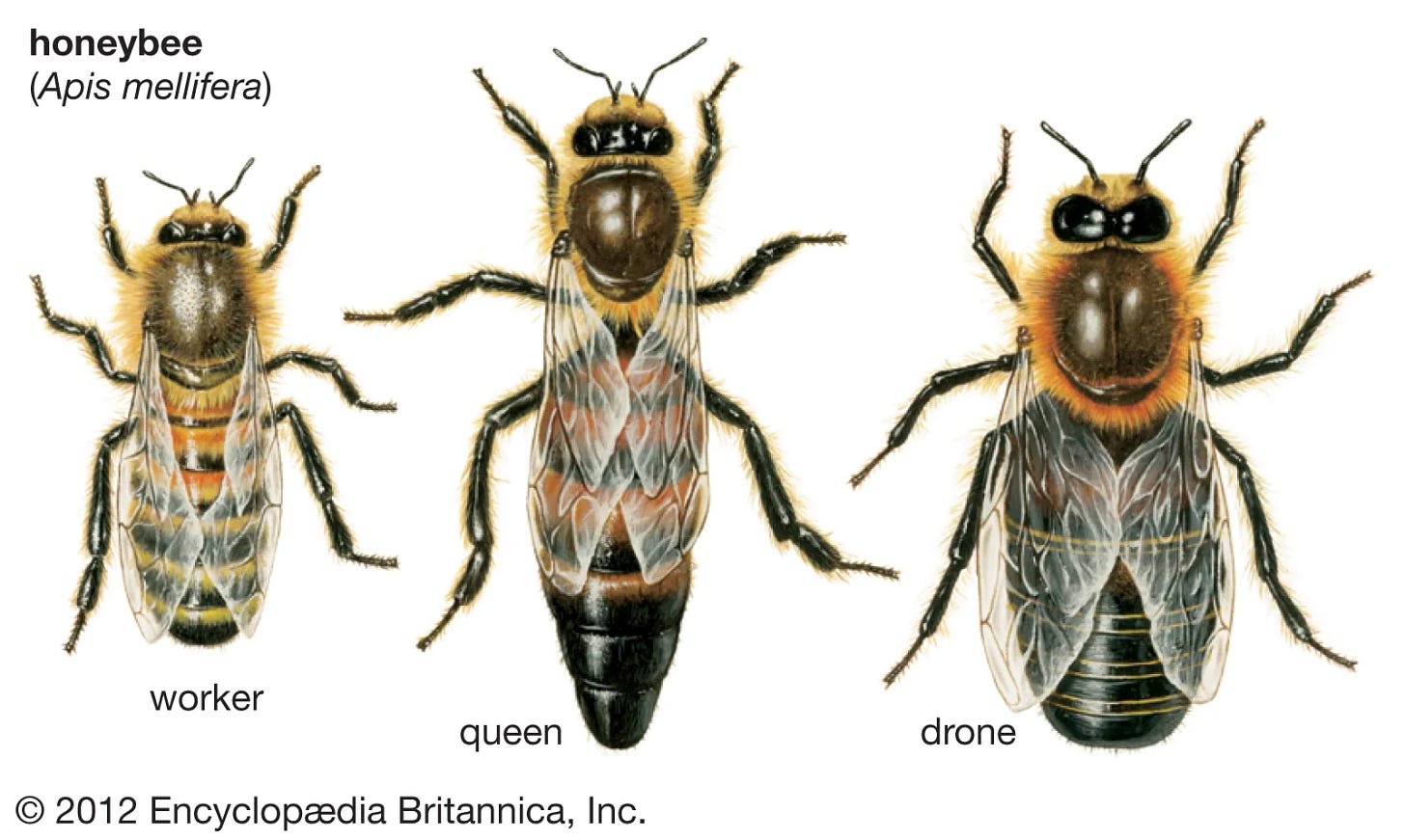
Drones can be easily distinguished from worker bees by their physical appearance. They are larger in size, have larger eyes, and lack stingers. Unlike worker bees, drones do not engage in foraging or hive-building activities and have a less pronounced role within the hive. Their physical characteristics are well-suited for their primary purpose of mating with queen bees.
Drone bee lifespan
The lifespan of a drone bee is relatively short compared to that of worker bees. While worker bees can live for several weeks, drones survive for only a few months. Their life cycle is closely linked to the mating season as they are primarily produced by the colony during the swarming season when new queens are hatched.
Development and maturation of drone bees
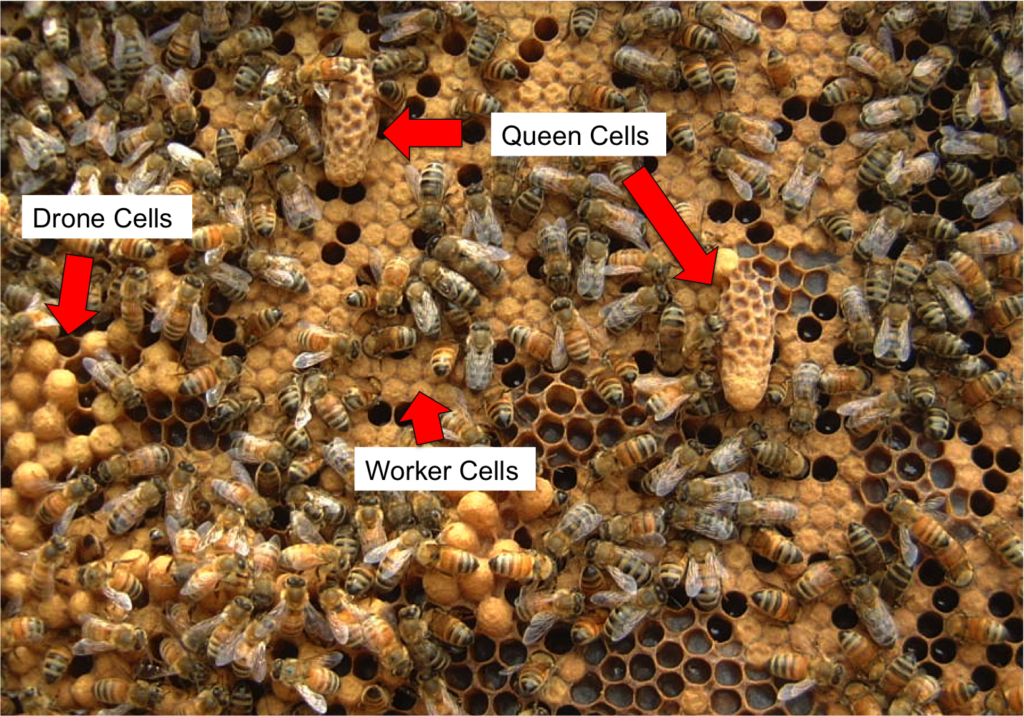
Drone bees undergo a unique development process within the hive. They are produced from unfertilized eggs laid by the queen. After hatching, drones go through several developmental stages before reaching sexual maturity. Once mature, they venture out of the hive to mate with queen bees from other colonies, contributing to the genetic variation of the honey bee population.
Drones’ unique reproductive organs
Drones possess distinct reproductive organs compared to worker bees. They have larger and more developed reproductive glands, called seminal vesicles, which store the sperm for mating. Additionally, drones have a specialized organ, the endophallus, which aids in successful mating with the queen bee. These unique reproductive adaptations enable drones to fulfill their essential role in bee reproduction.
Drone Congregation Areas (DCAs)
Definition and purpose of DCAs
Drone Congregation Areas (DCAs) are specific locations where drones from multiple hives gather to mate with queen bees. These areas serve as meeting points for drones, ensuring genetic exchange between colonies. DCAs are vital for maintaining genetic diversity within honey bee populations.
How DCAs are formed
DCAs are typically formed in regions with suitable environmental conditions, such as open spaces with good visibility and access to sunlight. These areas may be located near natural landmarks, such as hills or trees, which aid drones in orienting themselves. The collective pheromones released by the queen bees during mating influence the formation and location of DCAs.
Factors influencing DCA locations
Several factors influence the selection of DCA locations. Distance from the original hive, environmental conditions, availability of food sources, and the presence of other colonies all play a role in determining the attractiveness of an area to drones. The specific factors influencing DCA locations can vary depending on regional and local conditions.
The behavior and social interactions within DCAs
DCAs are dynamic and bustling locations where drones engage in social interactions. They engage in flight displays, releasing pheromones to attract queen bees and competing with other drones for mating opportunities. These social interactions are essential for the successful reproduction of honey bees and contribute to the overall genetic diversity of the population.
Mating Behavior of Drone Bees
Drone flights: purpose and characteristics
Drone flights are an integral part of the mating behavior of drone bees. Once they reach sexual maturity, drones leave the hive and embark on orientation flights to familiarize themselves with the surrounding area. These flights serve as practice sessions for future mating flights and provide drones with an understanding of their surroundings.
Recognition of virgin queen pheromones
Drones possess a remarkable ability to recognize and track the pheromones released by virgin queen bees. These pheromones act as powerful attractants, guiding drones towards the queen in need of mating. This recognition mechanism ensures that drones can locate the queen and fulfill their vital reproductive role.
Drone competition and mating strategies
Competition among drones for mating opportunities is fierce. As numerous drones gather in DCAs, they engage in competitive flight displays and pheromone releases to attract queen bees. Only a small percentage of drones successfully mate, underlining the importance of genetic quality and competitive strategies in the selection process.
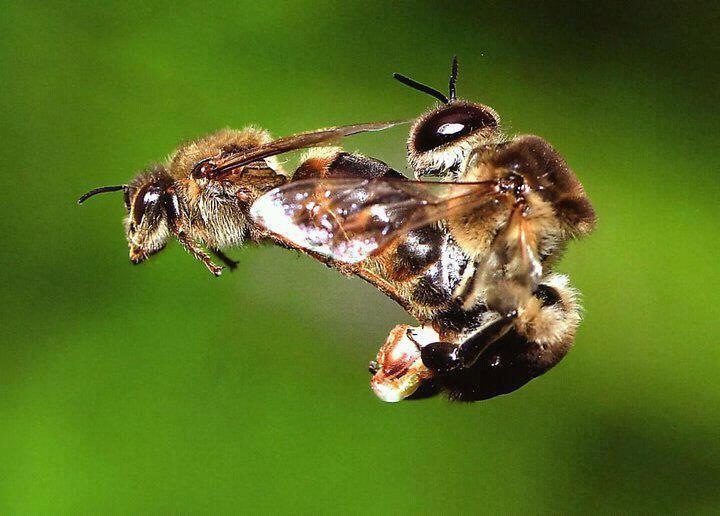
The process of drone mating with the queen bee
When a drone successfully mates with the queen bee, it transfers its stored sperm to the queen using its specialized reproductive organs. This single mating session is often fatal for the drone, as the endophallus gets detached and remains inside the queen, resulting in the drone’s death. Mating with the queen and transferring sperm ensures the successful fertilization of eggs and the continued growth of the colony.
Genetic Variation and Bee Colony Health
Importance of genetic diversity in bee colonies
Genetic diversity is vital for the resilience and health of bee colonies. It provides colonies with the ability to adapt to environmental changes, resist diseases and pests, and maintain a thriving population. Through mating with drones from other colonies, queen bees contribute to genetic diversity by introducing new traits and characteristics to the colony.
The effects of inbreeding on the colony
Inbreeding, which occurs when queen bees mate with drones from the same hive, can lead to detrimental effects on the colony. It decreases genetic diversity, making the colony more vulnerable to diseases and reducing its overall fitness. Inbreeding depression can manifest as decreased colony productivity, poor survival rates, and increased susceptibility to environmental stresses.
How drones contribute to genetic variation
Drones play a crucial role in maintaining genetic variation within honey bee populations. By mating with queen bees from different colonies, drones introduce genetic material from diverse sources, increasing the genetic variability of subsequent generations. This genetic exchange is essential for enhancing the overall adaptability of the colony.
Signs of a genetically diverse and healthy colony
A genetically diverse and healthy colony exhibits various signs. These include increased resistance to diseases and pests, efficient foraging behavior, and strong colony productivity. genetic diversity also contributes to a well-balanced and harmonious social structure within the hive, maximizing the chances of long-term survival and reproductive success.
The Role of Drones post-Mating
Drone mortality after mating
Mating is a consequential event for drones, as it often leads to their demise. After mating with the queen bee, the endophallus gets detached from the drone’s body, resulting in severe injuries and eventual death. This sacrifice highlights the unique purpose of drones in reproduction and their limited lifespan within the colony.
Efficiency of drones in breeding
Efficiency in breeding is a core aspect of the drone’s role within the colony. Drones are specialized for mating, and their reproductive organs are adapted for successful fertilization. The genetic contribution made by drones significantly impacts the colony’s overall reproductive success and long-term survival.
Drones as contributors to colony maintenance
Although drones primarily focus on mating, they also play a minor role in colony maintenance. Some drones assist in thermoregulation within the hive, ensuring optimal temperature conditions for brood development. However, their contribution in this regard is minimal compared to the vital functions carried out by worker bees.
The drone’s limited role within the hive
Compared to worker bees, drones have a limited role within the hive. They do not engage in foraging or hive-building activities and consume resources without actively contributing to the colony’s needs. As a result, worker bees regulate the production of drones based on the colony’s requirements, reflecting the drone’s secondary position in the social structure.
Challenges and Threats Faced by the Drone Population
Environmental factors affecting drone survival
Drone populations face several environmental challenges that affect their survival. Extreme temperatures, natural disasters, and changes in forage availability can all impact the availability of resources necessary for drone development and mating. Environmental conservation efforts are crucial in mitigating the adverse effects on drone populations.
Human activities impacting drone populations
Human activities can have significant negative impacts on drone populations. Habitat loss due to urbanization and agricultural intensification reduces the availability of suitable mating areas. Pesticide use can also have detrimental effects on drone populations, as exposure to these chemicals can impair their reproductive capabilities and overall health.
Pesticides and their impact on drones
Pesticides, including insecticides and herbicides, pose a substantial threat to drone populations. Direct exposure to these chemicals can lead to immediate mortality, while sublethal doses can impair drone fertility and weaken their immune systems. Reducing pesticide usage and implementing alternative pest management strategies are crucial for safeguarding drone populations.
Disease and parasites affecting drone health
Drones are susceptible to various diseases and parasites that can negatively impact their health and reproductive abilities. Varroa mites, Nosema ceranae, and viral infections are among the primary threats. Maintaining hive hygiene, implementing disease monitoring protocols, and utilizing appropriate treatment methods are essential for preserving the health and vitality of drones.
Conservation Efforts for Drones
Current initiatives for drone conservation
Recognizing the importance of drones in maintaining genetic diversity and healthy bee populations, several initiatives focus on drone conservation. Collaborations between beekeepers, researchers, and conservation organizations aim to promote sustainable beekeeping practices, protect natural habitats, and increase awareness of the role of drones in bee reproduction.
The importance of protecting drone populations
Protecting drone populations is crucial for the overall health and survival of honey bee colonies. Conservation efforts targeting drones contribute to the preservation of genetic diversity and the long-term viability of bee populations. By protecting drones, we ensure the continuity of their role in the reproductive cycle and the sustainability of honey bee populations.
Strategies for creating drone-friendly environments
Creating drone-friendly environments involves providing suitable habitats and forage resources. Planting diverse flowering plants, minimizing pesticide use, and preserving natural landscapes contribute to the creation of favorable conditions for drones. Implementing these strategies on a large scale can support the well-being and reproductive success of drones.
Collaborations between beekeepers and researchers
Collaboration between beekeepers and researchers is essential for the successful implementation of drone conservation strategies. Beekeepers’ practical insights combined with researchers’ scientific expertise can lead to the development of effective beekeeping practices that prioritize drone health and genetic diversity. These collaborations are vital for fostering a sustainable future for bees and the ecosystems they support.

The Implications for Beekeeping
Beekeeping practices and their influence on drones
Beekeeping practices have a significant influence on drone populations. Beekeepers manage colony size, control queen rearing, and select breeding programs that affect the number and genetic quality of drones within a hive. Adopting sustainable beekeeping practices that prioritize genetic diversity and drone well-being is crucial for the long-term success of beekeeping operations.
Optimizing drone production in beekeeping operations
Optimizing drone production involves carefully managing the colony’s reproductive cycle. Beekeepers strategically control the production of drones to minimize resource consumption and maximize genetic diversity. By understanding the natural cues and biology of honey bees, beekeepers can ensure that drones are produced and mated during the most favorable conditions.
How drones affect honey production
Drones have minimal direct impact on honey production within the hive. Since they do not engage in foraging activities, the burden of nectar and pollen collection rests solely on worker bees. However, the genetic diversity contributed by drones indirectly impacts the overall productivity and sustainability of honey bee colonies, ultimately influencing honey production.
Balancing drone rearing with worker bee colony needs
Maintaining a balance between drone rearing and the needs of the worker bee colony is essential. While drones play a vital role in reproduction, excess drone production can strain limited resources and compromise the productivity of worker bees. Beekeepers carefully manage the number of drones within a colony to optimize reproductive success while maintaining the colony’s overall health and productivity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, drones are unsung heroes of bee reproduction, playing a crucial role in the genetic diversity and survival of honey bee colonies. Understanding their characteristics, behaviors, and significance within the hive provides insights into the complex dynamics of bee reproduction. Protecting and preserving drone populations is essential for the long-term sustainability of honey bees and the ecosystems they contribute to. By recognizing the importance of drones and supporting conservation efforts, we can ensure the continued success of beekeeping and the overall health of honey bee populations. Continued research and collaborative initiatives are key to deepening our understanding of drones and implementing effective strategies for their conservation and preservation.