Are you curious about how bees can play a crucial role in saving our ecosystem? In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of beekeeping for sustainability and the incredible impact that bees have on our environment. From their essential role in pollination to the production of honey and other bee-derived products, we will unveil the vital importance of bees and how we can all contribute to their preservation. So grab a cup of tea and prepare to be amazed by the extraordinary contributions these little creatures make to our world.
The Importance of Bees in Our Ecosystem
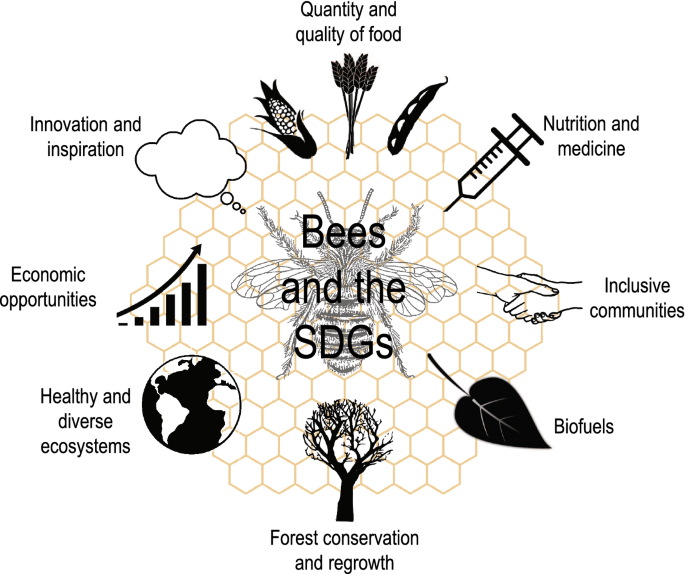
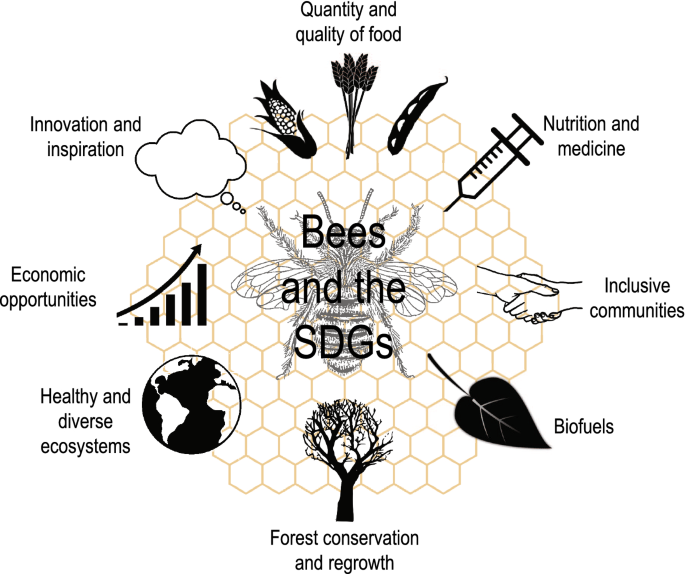
Bees play a vital role in our ecosystem, and their importance cannot be overstated. One of the key contributions of bees is their role in the pollination process. When bees move from flower to flower in search of nectar, they inadvertently transfer pollen from the male parts of the plant to the female parts, thereby enabling the plants to reproduce. This process ensures that plants can continue to produce fruits, vegetables, seeds, and nuts, which form the basis of our food chain.
Aside from their role in pollination, bees also contribute to biodiversity. By visiting a wide variety of flowers, bees help to sustain the diversity of plant species. This is important because a diverse plant population provides habitat and food for numerous other animal species. Bees also serve as pollinators for many wildflowers and plants that are crucial for maintaining a healthy ecosystem.
Furthermore, bees provide several environmental benefits. The pollination services they offer lead to greater plant growth, which improves air quality and reduces soil erosion. Bees are also responsible for cross-pollinating wildflowers, which is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems. Additionally, the honey produced by bees serves as a valuable food source for other animals, including mammals, birds, and insects.
The Threats to Bee Populations
Despite their crucial role in our ecosystem, bee populations worldwide are facing numerous threats. One major concern is the extensive use of pesticides and chemicals in agriculture. Pesticides not only compromise the health of bees but also contaminate their hive and food sources, leading to their eventual decline. The indiscriminate use of these chemicals has detrimental effects on the survival of not only honeybees but also wild bee populations.
Habitat loss is another significant threat to bee populations. As human activities, such as urbanization and intensive agriculture, continue to expand, natural habitats are being destroyed or fragmented. This loss of habitat reduces the availability of flowers and nesting sites for bees, making it challenging for them to survive and thrive.
Furthermore, diseases and parasites pose a significant threat to bee populations worldwide. Varroa mites, in particular, are a widespread problem and can weaken honeybee colonies by feeding off their blood and transmitting diseases. Other pests and diseases, such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, also contribute to the decline of bee populations.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Beekeeping as a Solution
Beekeeping, or apiculture, offers a practical solution to the threats faced by bees. By taking up beekeeping, individuals and communities can actively contribute to the conservation and preservation of these essential pollinators.
One way to promote beekeeping is by raising awareness and educating the public about the importance of bees and the threats they face. This can be done through workshops, campaigns, and educational programs. By highlighting the benefits of beekeeping and offering guidance on how to get started, more people can be encouraged to take up this rewarding hobby.
Creating bee-friendly gardens is another effective way to support bee populations. By planting a diverse range of native flowering plants, individuals can provide bees with a reliable source of nectar and pollen. Additionally, using organic and bee-friendly gardening practices, such as avoiding the use of pesticides, ensures that bees can thrive in these gardens.
Conserving natural habitats is crucial for the long-term survival of bees. By protecting and restoring wild and natural areas, we can provide nesting sites, forage, and safe havens for bees. This can be achieved through the establishment of protected areas, the creation of wildlife corridors, and the adoption of sustainable land management practices.
Benefits of Beekeeping for Sustainability
Beekeeping offers several benefits for sustainability, making it an attractive practice for individuals and communities alike. Increased pollination is one of the significant advantages of beekeeping. By actively managing bees, beekeepers can ensure that crops and wildflowers receive adequate pollination, resulting in higher yields and better-quality produce. This increased pollination can help address food shortages, enhance agricultural productivity, and ultimately contribute to food security.
Beekeeping also plays a crucial role in protecting endangered plant species. Many plants rely on specific bee species for pollination, and their decline can lead to the loss of these plants. Beekeepers can help safeguard these endangered plants by providing managed colonies of bees for pollination services, thereby ensuring the survival and conservation of these important plant species.
Furthermore, beekeeping contributes to enhanced food security. Honey, beeswax, and other bee products provide a valuable source of nutrition and income for beekeepers and their communities. Beekeeping also promotes sustainable agricultural practices, as it encourages a diverse range of flowering plants that provide habitats for other pollinators and beneficial insects. This, in turn, leads to overall ecosystem health and resilience.

This image is property of dailymom.com.
Steps to Start Beekeeping
Starting beekeeping requires research, education, and careful planning to ensure success. First and foremost, it is essential to research the local regulations and requirements related to beekeeping in your area. This will help you understand any legal constraints and obtain necessary permits or licenses.
Choosing the right location for your beekeeping operation is crucial. Bees require access to a diverse range of flowering plants and a water source nearby. Additionally, the location should be safe and free from potential disturbances, such as excessive noise, exposure to pesticides, or the presence of predatory animals.
Selecting the appropriate bee species for your region is another important consideration. Different bee species have different characteristics and behavior. Consult with local beekeepers or experts to determine which species are best suited for your climate and environment. Factors such as temperament, disease resistance, and honey production can influence your selection.
Beekeeping Equipment and Techniques
Beekeeping requires specific equipment and techniques to ensure the well-being of the bees and the success of the operation. The primary equipment used in beekeeping is the hive and frames. The hive serves as the home for the bees, while the frames provide structural support and allow for easy inspection and honey extraction. Hives can be made of wood or other materials, and there are various types to choose from, such as Langstroth hives or top-bar hives.
A smoker is an essential tool in beekeeping, used to calm the bees and reduce their defensive behavior during hive inspections. Additionally, beekeepers need to wear protective clothing, including a veil, beekeeping suit or jacket, gloves, and boots. These items protect the beekeeper from bee stings and minimize the risk of injury.
Honey extraction methods vary depending on the type of hive and frames used. Extracting honey usually involves removing the frames from the hive, uncapping the honey cells, and using a centrifugal force method to extract the honey. The extracted honey can then be filtered and stored for consumption or sale.

This image is property of www.bekarmic.com.
Supporting Bee Health
Maintaining the health and well-being of bees is crucial for their survival and the continued success of beekeeping operations. Providing adequate nutrition is one of the key factors in promoting bee health. This can be achieved by ensuring that bees have access to a diverse range of flowering plants throughout the seasons. Supplemental feeding may be necessary during times when natural nectar and pollen sources are scarce.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to manage pests and diseases in beekeeping. It involves a combination of preventive measures, cultural practices, biological controls, and, if necessary, the judicious use of chemical treatments. Regular monitoring for pests and diseases allows beekeepers to take timely action to mitigate their impact and ensure the health of their bee colonies.
Beekeepers should also participate in disease monitoring programs and stay up to date with the latest research and best practices in beekeeping. This allows for early detection and control of diseases and parasites, minimizing their impact on bee populations. Regular hive inspections, record-keeping, and collaboration with other beekeepers and experts are crucial in maintaining healthy bee colonies.
The Role of Beekeepers as Conservationists
Beekeepers have an essential role to play as conservationists. Beyond the day-to-day management of their bee colonies, they can actively contribute to the preservation of bee habitats and the health of wild bee populations.
educating the public about the importance of bees and their role in the ecosystem is a critical role for beekeepers. By raising awareness and dispelling myths and misconceptions, beekeepers can foster a greater appreciation for bees. This can be done through public presentations, workshops, and educational programs, targeting both children and adults.
Participating in research and citizen science initiatives allows beekeepers to contribute valuable data and insights into bee health and behavior. By sharing their experiences and observations, they can contribute to the scientific knowledge and understanding of bees. This collaboration between beekeepers and researchers is mutually beneficial and can lead to more effective conservation strategies.
Protecting natural bee habitats is another crucial responsibility of beekeepers. This can be done by supporting and advocating for the conservation of wild and natural areas, raising concerns about habitat destruction, and promoting sustainable land management practices. By preserving and restoring bee habitats, beekeepers can help ensure the long-term survival of bees and the pollination services they provide.

This image is property of www.ecowatch.com.
Community Beekeeping Initiatives
Community beekeeping initiatives have gained popularity in recent years, offering numerous benefits to both urban and rural communities. Urban beekeeping, in particular, has become a popular way to promote bee conservation and engage the public in sustainable practices.
School and educational programs focused on beekeeping provide students with valuable hands-on learning opportunities. Beekeeping can be incorporated into science curricula, teaching students about pollination, biodiversity, and environmental stewardship. These programs not only foster a sense of responsibility towards the environment but also provide students with practical skills and knowledge.
Collaboration with farmers is another community beekeeping initiative that can have significant positive impacts. By working together, beekeepers and farmers can ensure that crops receive adequate pollination services, resulting in higher yields and better-quality produce. Additionally, farmers can benefit from the honey and other bee products produced by the beekeepers.
Challenges and Solutions in Beekeeping
While beekeeping offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its fair share of challenges. One of the primary challenges in beekeeping is controlling Varroa mites. These parasitic mites weaken honeybee colonies and can transmit diseases. Regular monitoring, treatment, and the use of integrated pest management strategies are crucial in controlling these mites and maintaining healthy bee colonies.
Another challenge is managing queen bees. Queen bees are responsible for egg-laying and the overall performance of the colony. Beekeepers need to ensure the availability of healthy and productive queen bees to maintain the strength and productivity of their colonies. Techniques such as requeening, queen cell production, and queen selection help in managing queen bees effectively.
Dealing with swarming is another challenge in beekeeping. Swarming is the natural process by which a honeybee colony reproduces and splits into two or more colonies. While swarming is a natural part of a bee colony’s life cycle, it can be disruptive and result in the loss of bees. Beekeepers can manage swarming by providing adequate space for the colony, monitoring the hive for signs of swarming, and utilizing techniques such as swarm prevention and swarm capture.
In conclusion, bees play a vital role in our ecosystem, and their conservation is crucial for the sustainability of our food systems and biodiversity. Beekeeping offers a practical solution to the threats faced by bees, promoting pollination, protecting endangered plants, and enhancing food security. By supporting bee health, educating the public, and preserving natural habitats, beekeepers also contribute to the conservation of bees and their habitats. Community beekeeping initiatives and collaborations with farmers further strengthen the impact of beekeeping efforts. Despite the challenges faced in beekeeping, with proper research, education, and techniques, it is possible to overcome these hurdles and ensure the long-term survival of bees and our ecosystem. So, why not join the buzzing community of beekeepers and be a part of the solution? Your actions can make a significant difference in saving our ecosystem.
Word Count: 2285 words.

This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.