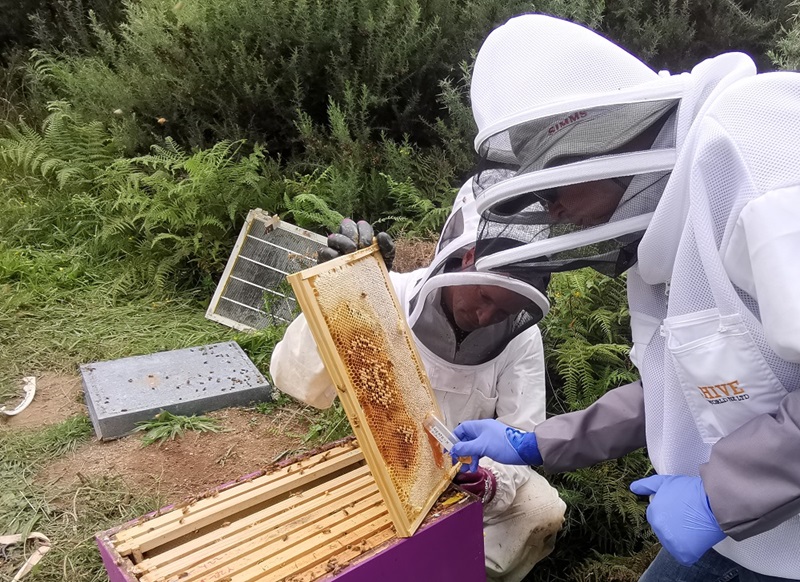

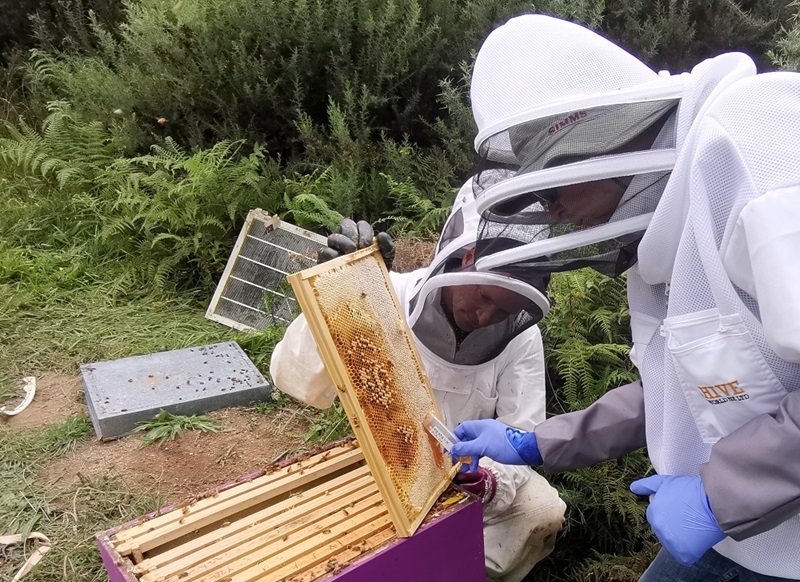
Imagine a world without honey bees. No more sweet golden honey drizzled on warm biscuits, no more vibrant flowers blooming in the spring, and certainly no more juicy fruits to enjoy. Honey bees play a crucial role in our ecosystems, pollinating plants and crops that sustain our food supply. But they face a relentless enemy: the Varroa mite. This harmful parasite has been wreaking havoc on honey bee populations worldwide, causing devastating losses. Thankfully, the National Science Agency in Australia is on a mission to protect these important pollinators. Through innovative research on Australia’s native bee species, genomic studies on the Varroa mite, and the use of honey bees as environmental monitors, they are paving the way for understanding and combating this tiny but mighty threat. So, join the fight and discover how you can help save the bees!

This image is property of www.csiro.au.
Research on Australia’s Native Bee Species
Australia is renowned for its diverse wildlife, and its native bee species are no exception. The National Science Agency in Australia is dedicated to protecting these bees and ensuring their survival in the face of various challenges. One area of focus for researchers is the study of Australia’s native bee species, which provides valuable insights into their behavior, ecology, and role in the ecosystem.
Studying the native bee species
Researchers are actively studying the behavior and characteristics of Australia’s native bees to better understand their unique biology. By observing and recording their foraging habits, nesting behaviors, and interaction with other organisms, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of their ecological role. This research also helps identify any threats they may face and develop strategies for their conservation.
Focus on the giant specimen
Among the many fascinating native bee species in Australia, the giant specimen holds a special place of intrigue. However, the illegal trade of this bee species has posed a significant threat to its population. Researchers are working diligently to protect this giant bee from the detrimental effects of illegal trade. By studying its biology, habitat requirements, and ecological role, scientists hope to develop effective conservation strategies to safeguard its future.
Illegal trade and its impact on the species
The illegal trade of the giant bee species in Australia has had devastating consequences for its population. International demand for these unique insects has driven their capture and trafficking, leading to a decline in their numbers. The National Science Agency is collaborating with law enforcement agencies to crack down on the illegal trade and protect the giant bee from further harm. This research brings attention to the importance of legal measures and international cooperation to combat the illegal wildlife trade and preserve biodiversity.
Environmental Monitoring Using Bees
In recent years, bees have shown great potential as environmental monitors through the use of environmental DNA (eDNA) testing. This innovative approach allows scientists to detect and analyze the genetic material shed by organisms into their environment. By utilizing bees as environmental monitors, researchers can gain valuable insights into the overall health of ecosystems and the presence of specific species.
Overview of environmental DNA (eDNA) testing
Environmental DNA testing involves collecting and analyzing DNA fragments that organisms release into their surroundings. This genetic material can be found in various forms, such as skin cells, feces, or secretions. By taking samples from the environment, scientists can extract DNA and identify the organisms present, even without directly observing them. This non-invasive method has revolutionized ecological research by providing a wealth of information about species diversity and ecosystem dynamics.
Utilizing bees as environmental monitors
The unique foraging behavior of bees makes them excellent candidates for eDNA testing. Bees collect nectar and pollen from a wide range of flowering plants, inadvertently picking up traces of DNA from those plants in the process. By sampling the bees themselves, researchers can discover which plant species they visit and thus gain insights into the overall flowering vegetation in a given area. This information is invaluable for monitoring changes in plant communities and tracking the impact of environmental disturbances on ecosystem health.
Applications of eDNA testing in bee research
In addition to monitoring flowering vegetation, eDNA testing conducted on bees can provide insights into other aspects of their ecology. For example, scientists can analyze the genetic material present in bees’ digestive tracts to determine the diversity of nectar and pollen sources they rely on. This information helps identify the plants that are vital for the bees’ nutrition and overall well-being. Furthermore, eDNA testing can also be used to detect the presence of pathogens or parasites in bee populations, aiding in early disease detection and effective management strategies.
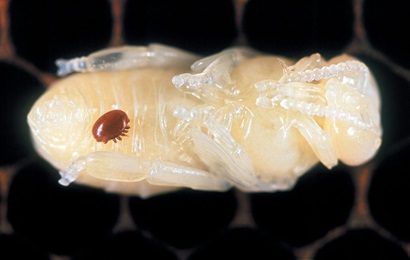
Understanding the Varroa Mite
The Varroa mite, a harmful parasite, poses a significant threat to honey bees worldwide. In Australia, the National Science Agency is actively conducting research on the Varroa mite to understand its genomic makeup, its spread, and its impact on honey bee colonies.
Genomic research on the Varroa mite
Genomic research plays a vital role in understanding the Varroa mite’s biology and its interactions with honey bees. By sequencing and analyzing the mite’s genome, researchers can pinpoint the genes that make it such a destructive parasite. This knowledge can then be used to develop targeted interventions and management strategies to mitigate the mite’s impact on honey bee populations.
Investigating the spread and impact of the mite
The Varroa mite is known to spread rapidly, devastating honey bee colonies in its path. Scientists are investigating the mechanisms and pathways through which the mite spreads to gain insights into preventing its further expansion. By understanding the mite’s dispersal patterns, researchers can develop strategies to limit its movement and protect vulnerable honey bee populations. Furthermore, studying the mite’s impact on honey bee colonies helps identify factors that make certain populations more vulnerable, facilitating the development of measures to enhance bee health and resilience.
Relationship between the mite and honey bee colonies
The relationship between the Varroa mite and honey bee colonies is complex and multifaceted. The mite feeds on the blood of adult bees and reproduces within developing bee larvae, weakening and ultimately killing the bees. This parasitic interaction poses a serious threat to honey bee colonies and their productivity. Additionally, the mite also acts as a vector for various viruses, further contributing to the decline in honey bee health. Studying the intricate dynamics between the mite and honey bees is crucial for developing effective control measures and saving these vital pollinators.
Role of Native Bees in Pollination
Native bees play a vital role in Australia’s ecosystems, particularly in pollinating native plants and crops. Understanding their importance and the threats they face is crucial for conserving these invaluable pollinators.
Importance of native bees in pollinating native plants
Australia is home to a rich diversity of native plant species, many of which rely on native bees for pollination. Native bees have co-evolved with these plants, developing unique relationships that ensure the plants’ reproductive success. They carry pollen from one flower to another, facilitating cross-pollination and the production of seeds and fruits. This process maintains the genetic diversity of plant populations and supports the overall health and resilience of native ecosystems.
Contribution to crop pollination
Native bees also contribute significantly to crop pollination, benefiting agricultural sectors in Australia. While honey bees are commonly used for crop pollination, native bees play a complementary role by increasing pollination efficiency and enhancing yields. Research has shown that certain native bee species are highly effective at pollinating specific crops, such as tomatoes, blueberries, and macadamia nuts. By promoting the presence and abundance of native bees in agricultural landscapes, farmers can improve crop productivity and reduce reliance on imported honey bees.
Threats to native bee populations
Despite their importance, native bee populations in Australia are facing numerous threats. Habitat loss, pesticide exposure, climate change, and competition with introduced bee species all contribute to the decline of native bees. The National Science Agency is actively researching these threats and their impact on native bee populations to develop effective conservation strategies. By identifying key areas for habitat preservation, promoting sustainable farming practices, and raising awareness about the importance of native bees, scientists are working towards preserving these essential pollinators for future generations.
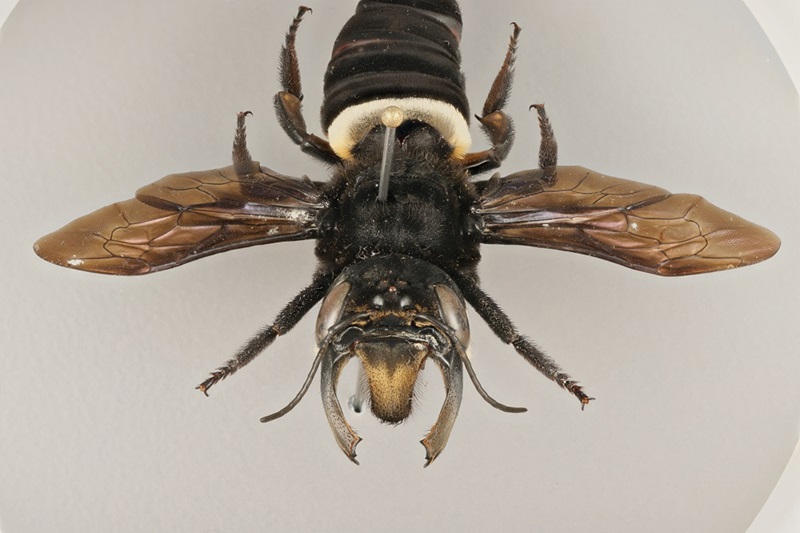
This image is property of www.csiro.au.
Protection of the Wallace’s Giant Bee
The Wallace’s Giant Bee (Megachile pluto) holds the distinction of being the largest bee in the world. However, this remarkable species is currently facing a significant threat due to illegal trade. Efforts are underway to protect this unique bee and ensure its survival.
Vulnerability of the Wallace’s Giant Bee to illegal trade
The Wallace’s Giant Bee is highly sought after by collectors and enthusiasts due to its impressive size and rarity. Unfortunately, this has led to illegal trading of the species, exacerbating the decline of its population. The National Science Agency is collaborating with law enforcement agencies to address this issue, emphasizing the need for stringent regulations and enforcement to combat the illegal wildlife trade effectively.
Conservation efforts and monitoring
Conservation efforts for the Wallace’s Giant Bee focus on preserving its natural habitat and reducing the impact of illegal trade. Research is being conducted to identify the bee’s preferred nesting sites and foraging areas, helping establish protected areas and conservation programs. Additionally, ongoing monitoring programs track the bee’s population status and distribution, helping inform conservation strategies and identify areas where intervention is urgently needed.
Promoting awareness about the species
Raising awareness about the Wallace’s Giant Bee is crucial to its protection. Outreach programs and educational initiatives are being implemented to inform the public about the bee’s ecological importance and the need to prevent its illegal trade. By engaging local communities, schools, and conservation organizations, researchers hope to foster a sense of stewardship and inspire active participation in the conservation of this iconic species.
Bees as Monitors of Flowering Vegetation
In addition to their role as pollinators, bees are proving to be invaluable in monitoring flowering vegetation. By collecting and analyzing pollen DNA, scientists can gain insights into plant communities, detect plant pathogens, and assess ecosystem health.
Monitoring flowering vegetation through bees
Bees are natural collectors of pollen as they forage on flowers. Researchers can utilize this behavior to monitor the diversity and abundance of flowering plants in a given area. By capturing pollen samples from bees and analyzing their DNA, scientists can identify the plant species the bees have visited. This information provides valuable data on the composition of plant communities and how they may change over time, aiding in the study of ecosystem dynamics and potential environmental shifts.
Pollen DNA testing to detect plant pathogens
Beyond monitoring flowering vegetation, bees can also serve as sentinels for detecting plant pathogens. Pollen carries the genetic material of plants, including harmful pathogens that can cause diseases. By analyzing the DNA present in pollen collected by bees, scientists can identify the presence of potential plant pathogens before they cause visible damage. Early detection allows for timely intervention and management strategies to prevent the spread of disease and protect vital plant species.
Benefits and challenges of using bees for monitoring purposes
Using bees as monitors of flowering vegetation offers several benefits. They provide a cost-effective and efficient method for collecting large quantities of pollen samples from various locations. Additionally, bees offer a holistic perspective on plant communities as they visit a wide range of flowering species. However, challenges such as sample contamination and the need for standardized protocols must be addressed to ensure the accuracy and reliability of pollen DNA testing. Ongoing research and collaboration are essential to refine techniques and overcome these challenges, unlocking the full potential of bees as valuable environmental monitors.

This image is property of www.csiro.au.
Encouraging Youth Participation in Bee Research
To advance the field of bee research, it is crucial to engage young people and inspire them to consider careers involving bees. The National Science Agency is actively promoting the importance of taxonomy and supporting aspiring researchers in the field.
Importance of taxonomy in bee research
Taxonomy, the science of classifying and naming organisms, plays a vital role in bee research and conservation. By accurately identifying and classifying bee species, scientists can understand their ecological role, track population trends, and inform conservation strategies. The National Science Agency recognizes the value of taxonomy and emphasizes its importance in bee research, highlighting the need for skilled taxonomists to contribute to the field.
Promoting careers involving bees
To encourage youth to pursue careers involving bees, the National Science Agency is actively promoting the diverse opportunities available in the field of bee research. From taxonomy and genetics to ecology and conservation, there are numerous pathways for young researchers to make significant contributions. Through mentorship programs, internships, and educational initiatives, the agency aims to inspire the next generation of scientists to explore the world of bees and contribute to their conservation.
Supporting young researchers in the field
The National Science Agency recognizes the importance of supporting and nurturing young researchers in the field of bee research. Scholarships, grants, and research opportunities are provided to encourage young scientists to pursue their passion for bees. By fostering a supportive environment and providing resources and mentorship, the agency aims to facilitate the growth and development of young researchers, ensuring a vibrant and collaborative bee research community.
In conclusion, the National Science Agency in Australia is conducting extensive research to protect honey bees from the Varroa mite and conserve Australia’s native bee species. By studying native bees, understanding the Varroa mite’s impact, recognizing the role of native bees in pollination, protecting endangered species like the Wallace’s Giant Bee, utilizing bees as environmental monitors, and encouraging youth participation in bee research, the agency is actively working towards the preservation of these vital pollinators and the ecosystems they support. Through ongoing research and collaboration, strides are being made to ensure the future vibrancy and sustainability of Australia’s bee populations.