Are you intrigued by the fascinating world of bees? In this article, we will explore the intricate and complex eyes of these remarkable creatures. Bees possess a unique visual system, characterized by an array of tiny, hexagonal facets known as ommatidia. Join us on this captivating journey as we unravel the secrets behind their unique vision. Prepare to be amazed by the wonder of nature and gain a deeper understanding of the bees’ fascinating world.
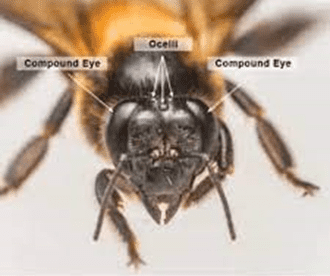
Anatomy of Bee Eyes
bees have a unique set of eyes that differ from the eyes of other insects. Their eyes are composed of thousands of tiny units called ommatidia, which make up a remarkable structure known as a compound eye. Unlike humans and many other animals, bees do not have just two large eyes but rather a series of small, individual lenses that work together to create a mosaic-like image of the world around them.
Compound Eyes vs. Simple Eyes
The compound eyes of bees offer several advantages over simple eyes found in other organisms. While simple eyes, also known as ocelli, are mainly responsible for detecting light and dark, compound eyes provide bees with a more sophisticated visual system. Each ommatidium in a bee’s compound eye functions as an individual photoreceptor, detecting and processing visual information. This allows bees to have a wide field of view and detect movements from various directions simultaneously.
Structure of a Compound Eye
A bee’s compound eye consists of numerous hexagonal ommatidia, packed tightly together to form a dome-like shape. Each ommatidium contains a lens, a cornea, and a series of light-sensitive cells. The lens helps to focus incoming light onto the photoreceptor cells, while the cornea acts as a protective outer layer. The photoreceptor cells, known as retinula cells, are responsible for converting incoming light into electrical signals that can be processed by the bee’s brain. The structure of a compound eye allows bees to perceive images in a fragmented manner, which contributes to their unique visual abilities.
How Bees See Colors
Bees have a remarkable ability to perceive and differentiate colors, an essential skill for their foraging activities. Their color vision, however, differs significantly from that of humans.
The Role of Photoreceptor Cells
Bees have three types of photoreceptor cells, known as trichromatic vision, which allows them to see a broader range of colors than humans. While humans have three different types of cone cells responsible for perceiving red, green, and blue, bees have cone cells that are sensitive to ultraviolet (UV), blue, and green light. This specialization in photoreceptor cells gives bees the ability to distinguish colors that are invisible to the human eye, such as ultraviolet patterns on flowers.
Ultraviolet Light Detection
One of the most fascinating aspects of bee vision is their ability to detect ultraviolet light. Many flowers have unique ultraviolet patterns that are invisible to humans but highly visible to bees. These patterns serve as visual guides for bees, directing them towards the nectar-rich parts of the flower. By detecting and interpreting these UV patterns, bees can efficiently locate and collect nectar from flowers, highlighting the crucial role of their specialized color vision in their foraging behavior.
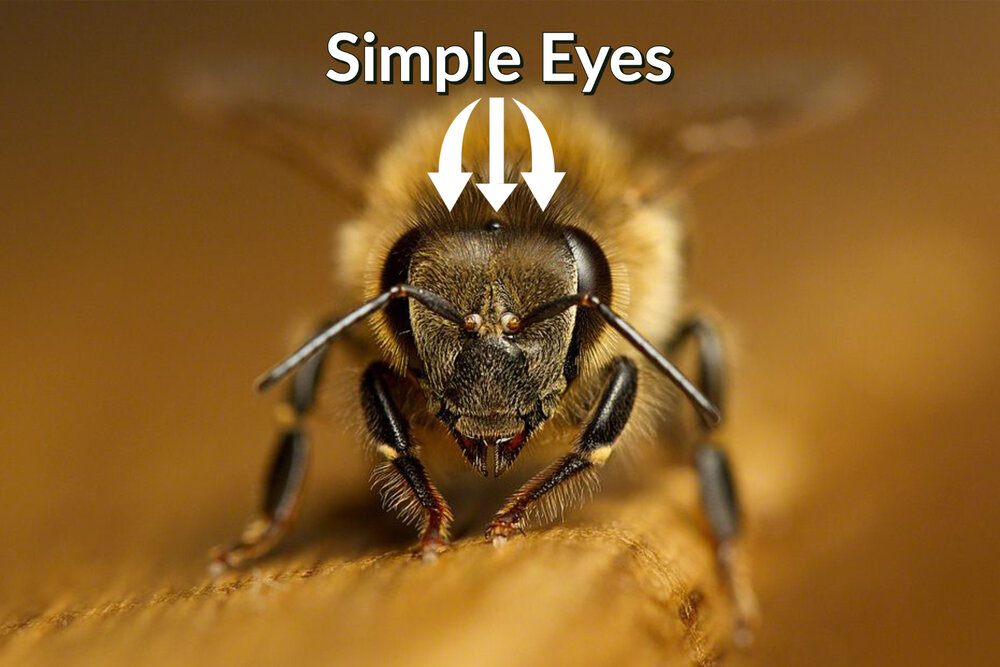

This image is property of images.squarespace-cdn.com.
Polarization Vision in Bees
In addition to their impressive color vision, bees possess another visual ability known as polarization vision. This unique skill allows them to perceive and navigate using polarized light.
Polarized Light
Light waves can vibrate in various directions, and polarization refers to the orientation of these vibrations. Bees can detect and interpret the patterns of polarized light in their environment, providing them with additional visual information that aids in their navigation and foraging. Polarized light patterns can be found in the sky, on water surfaces, and even on certain plants. By utilizing polarization vision, bees can accurately distinguish various objects and detect hidden structures, enabling them to navigate more effectively in their surroundings.
Specialized Polarization Vision
Bees have specific adaptations that enable them to utilize polarization vision effectively. Certain structures within their compound eyes, such as specialized receptors and layers of cuticle, help bees detect and analyze polarized light. These adaptations enhance their ability to perceive subtle changes in polarization and make use of this information for tasks such as orienting themselves within their habitat or locating food sources.
Motion Detection and Perception
Bees are not only specialized in perceiving colors and polarized light but are also highly skilled in detecting and processing motion.
Fast Visual Processing
One remarkable aspect of bee vision is their ability to process visual information rapidly. The individual ommatidia in a bee’s compound eye contribute to this impressive feat. As the ommatidia capture small sections of the visual field, bees can quickly detect and respond to even the slightest movements. This rapid visual processing allows bees to react promptly to potential threats or opportunities.
Optic Flow and Motion Detection
Bees rely on a phenomenon called optic flow to detect and interpret motion. Optic flow refers to the pattern of apparent motion generated when an observer moves through a dynamic environment. Bees use this optic flow to navigate accurately and efficiently, allowing them to fly smoothly and avoid obstacles. By continuously monitoring the optic flow, bees can make precise adjustments to their flight path, ensuring they reach their destination with remarkable accuracy.
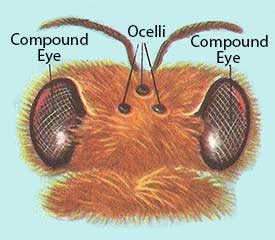
This image is property of wisconsinpollinators.com.
Adaptations for Efficient Vision
The unique anatomy of a bee’s eyes is not the only factor contributing to their exceptional vision. Bees have developed several adaptations that optimize their visual capabilities.
Facets and Resolution
The compound eyes of bees consist of thousands of facets or ommatidia, which enable them to perceive a broad visual field. However, this multitude of ommatidia comes at the cost of reduced resolution. Each ommatidium contributes a small, fragmented portion of the overall image. To compensate for this, bees rely on the sheer number of ommatidia and their ability to integrate visual information from multiple sources. This adaptation allows bees to create a cohesive and detailed image despite the individual limitations of each ommatidium.
Multiple Photoreceptor Types
Having multiple types of photoreceptor cells in their compound eyes provides bees with enhanced color vision. By detecting a broader range of wavelengths, bees can accurately perceive and differentiate between colors that may appear similar to humans. This multifaceted color vision plays a crucial role in their foraging activities, where the ability to identify specific flower colors guides them towards the most rewarding nectar sources.
Lack of Depth Perception
While bees possess exceptional visual abilities, they lack the depth perception that many organisms, including humans, rely on.
Lack of Binocular Vision
Unlike humans, who have overlapping visual fields from both eyes, bees lack binocular vision. Each compound eye functions independently, perceiving a slightly different visual field. This lack of overlap between the eyes makes it challenging for bees to perceive depth accurately. However, bees have adapted alternative strategies to overcome this limitation and navigate their environment successfully.
Alternative Depth Cues
Bees utilize various alternative cues to compensate for their lack of binocular vision and infer depth. One such cue is motion parallax, which refers to the apparent movement of objects at different distances as the bee moves. By observing the relative speed and direction of objects as they move, bees can judge their distance and position accurately. Additionally, bees also rely on size and perspective cues to estimate depth, allowing them to navigate obstacles and locate specific objects, including flowers, with remarkable precision.
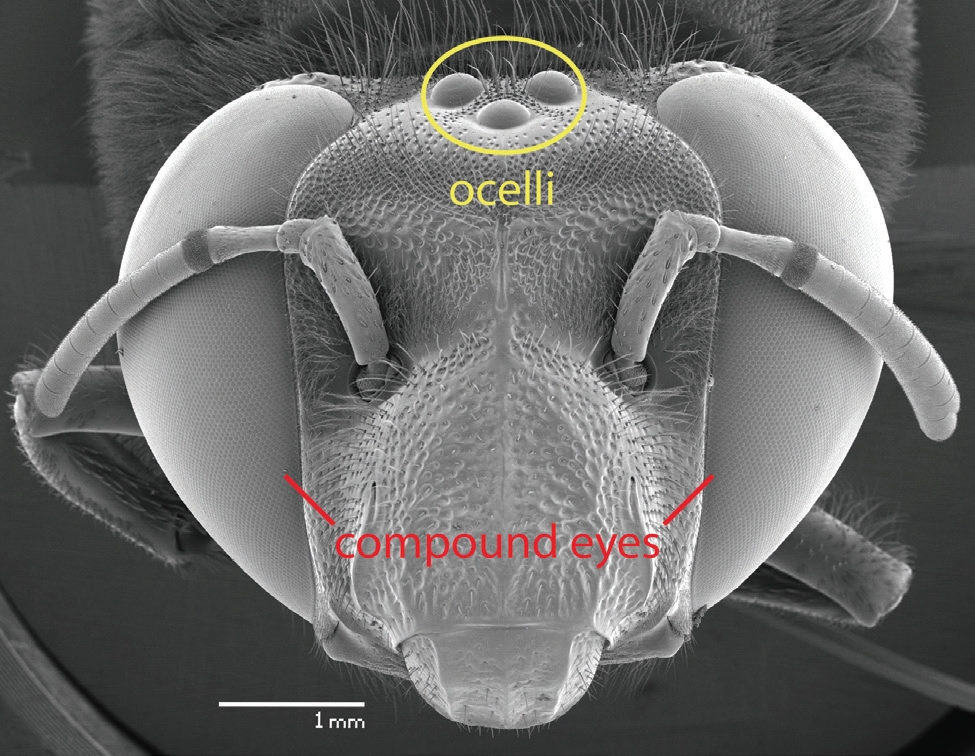
This image is property of www.diamond.ac.uk.
Bee Vision and Flower Selection
The remarkable visual abilities of bees play a crucial role in their interactions with flowers.
Flowers in UV Light
bees perceive and interpret the world of flowers differently than humans. Flowers often have distinct patterns visible under ultraviolet light. While these patterns are invisible to humans, bees can readily detect and interpret them. These unique UV patterns serve as attractive signals to bees, guiding them towards the nectar-rich areas of the flowers. The ability to perceive these UV patterns gives bees a competitive advantage when foraging for food and selecting the most rewarding flowers.
Nectar Guides
Many flowers have evolved specific visual cues known as nectar guides, which help attract bees and guide them towards the nectar. These guides can take the form of lines, spots, or other patterns on the flowers. Bees are particularly sensitive to these patterns, which contrast against the background of the flower. By following the nectar guides, bees can efficiently locate the nectar source within the flower, ensuring an optimal food-gathering process for both the bee and the plant.
Vision in Bee Navigation
Bees heavily rely on their exceptional vision for navigation, whether it be within their immediate surroundings or during long-distance flights.
Landmarks and Route Recollection
Bees possess a remarkable ability to recognize and remember specific landmarks in their environment. They can identify prominent features, such as trees, buildings, or distinctive natural formations, and use them as reference points for navigation. By relying on these landmarks, bees can accurately determine their location and find their way back to the hive or a known food source.
Polarized Sky Navigation
In addition to landmarks, bees also rely on the polarization pattern of the sky for navigation. By detecting and analyzing the polarization of skylight, bees can determine their heading and maintain a straight flight path. This ability is particularly useful on cloudy days or in areas where landmarks may be scarce. By utilizing the polarization of sunlight, bees have developed a reliable navigational tool that allows them to navigate with precision even in changing or unfamiliar environments.

This image is property of i1admin04.webstorepackage.com.
Challenges in Bee Vision Research
Studying how bees perceive and interpret their environment presents numerous challenges to researchers.
Studying Bee Vision Experimentally
Investigating bee vision requires specialized equipment and techniques. Researchers often rely on complex setups, such as specially designed arenas or flight simulators, to study bee behavior in controlled environments. Additionally, capturing and analyzing the rapid visual processing of bees can be an intricate task, requiring high-speed cameras and sophisticated algorithms to measure and interpret their responses accurately.
Technological Limitations
Despite advances in technology, there are still certain limitations in studying bee vision. For example, replicating a bee’s compound eye with its thousands of individual ommatidia is a challenging feat. The sheer complexity and miniature size of the compound eye make it difficult to examine the detailed structures and functions of each ommatidium. Furthermore, understanding the intricate neural pathways and processing mechanisms involved in bee vision poses significant challenges, as the bee’s brain is much smaller and less understood compared to other model organisms.
Applications of Bee Vision Research
The study of bee vision not only enhances our understanding of these fascinating creatures but also has practical applications in various fields.
Insights for Robotics and Computer Vision
The unique visual abilities of bees have inspired researchers in the field of robotics and computer vision. By studying and replicating the principles of bee vision, scientists aim to develop advanced algorithms and technologies that can enhance robotic vision systems. The ability to process visual information quickly and efficiently, as bees do, can have significant implications for applications such as autonomous navigation, object recognition, and even surveillance systems.
Development of Bee-Friendly Pesticides
Understanding how bees perceive and interact with their environment can have a direct impact on the development of bee-friendly pesticides. By studying how certain chemicals or pesticides affect bee vision, scientists can identify substances that pose minimal risk to bees while still effectively targeting harmful pests. This research can contribute to the development of more sustainable and environmentally friendly pesticide solutions, ensuring the continued well-being of bee populations and the ecosystems they support.
In conclusion, the complex eyes of bees provide them with remarkable visual abilities that allow them to perceive and interact with the world in unique ways. From their specialized color and polarization vision to their extraordinary motion detection and navigation skills, bees’ eyes have evolved to suit their specific needs. While challenges remain in studying and understanding bee vision, the insights gained from this research hold great potential for applications in robotics, computer vision, and the development of more environmentally friendly pesticides. By unraveling the mysteries of bee vision, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the extraordinary capabilities of these tiny but vital creatures.
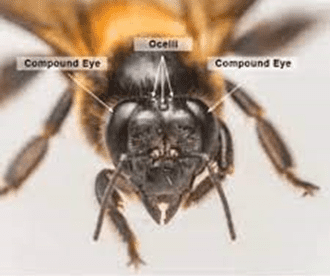
This image is property of www.ejbees.com.